
DiVYA
PHONE : +91-8374485833,
Mail : storagetanks@mail.com
INDUSTRIAL PIPING DESIGN CONULTANCY SERVICES

Steam Piping Design Services
Piping Design consultancy services- Steam Piping| Divya Engineering
"Divya Engineering offers expert piping design consultancy services specializing in steam piping systems. We provide innovative and cost-effective solutions tailored to your project needs
Steam piping refers to the network of pipes used to transport steam from a boiler (where it is generated) to various systems or equipment that require steam for heating, power generation, or other industrial processes. Steam is typically used in many industries, including power plants, chemical processing, heating systems, and manufacturing. Proper design, installation, and maintenance of steam piping systems are crucial for safety, efficiency, and performance.
Here are the key components and considerations in steam piping:
1. Types of Piping Materials
-
Carbon Steel: Common for steam systems due to its balance of strength, cost, and corrosion resistance.
-
Stainless Steel: Used in higher-temperature and more corrosive environments.
-
Alloy Steels: Can be used for higher pressure and temperature systems.
-
Copper or Copper Alloys: Sometimes used for smaller, lower-pressure steam systems.
2. Steam Pressure & Temperature
-
The piping system is designed based on the expected pressure and temperature of the steam. Steam pressure typically ranges from low-pressure (15–50 psi) to high-pressure systems (up to 1,500 psi or more).
-
Saturated Steam: Steam at the boiling point.
-
Superheated Steam: Steam that has been heated beyond its boiling point and is used in power generation and industrial processes.
3. Insulation
-
Insulating steam pipes helps to maintain steam temperature and prevent heat loss.
-
It also helps protect workers from heat burns and conserves energy.
-
Materials like fiberglass, mineral wool, or calcium silicate are commonly used for insulation.
4. Valves and Fittings
-
Various types of valves (e.g., ball valves, globe valves, check valves) are used to control the flow of steam, prevent backflow, and isolate sections of the system for maintenance.
-
Fittings like elbows, tees, and reducers are essential to change the direction or size of the piping.
5. Steam Traps
-
Steam traps remove condensate (water that forms when steam cools) from the system.
-
They ensure that steam flows efficiently by preventing water from accumulating in the pipes, which can cause damage or reduce performance.
6. Expansion Joints
-
These are used to accommodate the thermal expansion of pipes due to the high temperature of the steam.
7. Maintenance Considerations
-
Regular inspection for leaks, corrosion, or blockages is vital.
-
Proper sealing is necessary to avoid energy losses and reduce the risk of steam leaks, which can be dangerous at high pressures and temperatures.
8. System Design and Layout
-
The steam piping layout should minimize pressure drops and ensure efficient steam flow.
-
Pipe sizing, material selection, and route planning are important factors to consider for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
If you're dealing with a specific steam piping system or need help with design, troubleshooting, or installation, feel free to ask more specific questions!
PIPING DESIGN AND DRAFTING
Creating detailed CAD drawings and design calculations for deferent steam piping systems, including those used in oil and gas, petrochemicals, power plants, and storage tanks.
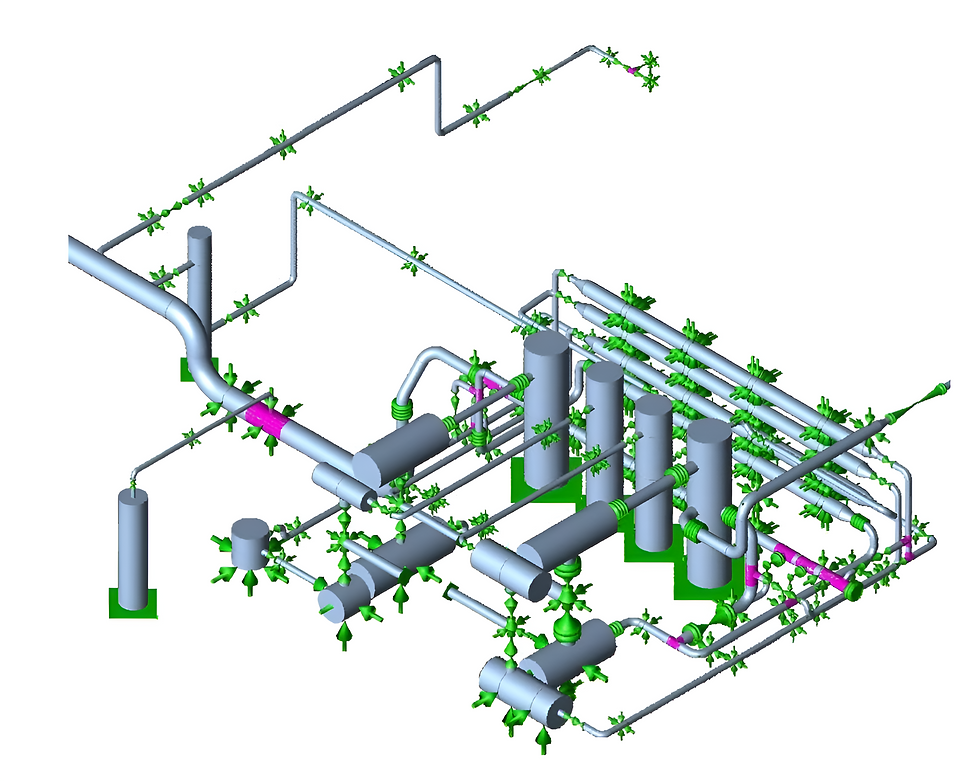
PIPING LAYOUT AND ROUTING
This involves determining the optimal layout and routing of pipes to ensure efficient flow, minimize pressure drop, and avoid interference with other equipment or structures. Additionally

PIPING SUPPORT DESIGN
designing and specifying supports to properly secure and support the piping system, preventing excessive stress and vibration, is an essential aspect of the design process

PIPING MATERIAL SELECTION
Piping Material Selection: Selecting the most suitable steam pipe materials based on factors such as the fluid being transported, operating temperature and pressure, and potential corrosion risks. This also involves considering factors like material availability, cost, and compatibility with industry standards to ensure the longevity and safety of the system.

PIPING STRESS ANALYSIS
Piping Stress Analysis: Performing static and dynamic stress analysis using specialized software like CAESAR II to assess how the steam piping system will respond to both operational and environmental stresses. This process helps identify potential areas of failure and ensures that the steam piping system remains structurally sound under varying conditions
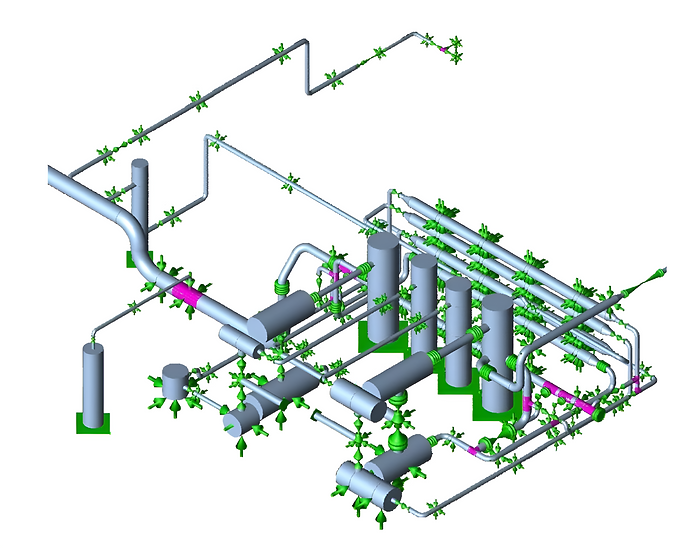
PIPING AND INSTRUMENTATION DIAGRAMS (P&IDS):
Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs): Developing P&IDs to provide a clear representation of the steam piping system, including all components, instrumentation, and control systems. These diagrams serve as essential tools for ensuring proper integration of the system's functions and are a vital reference during both construction and operation phases
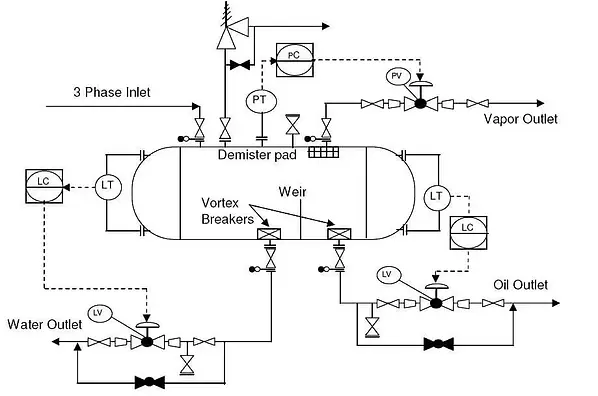
DEVELOPMENT OF PIPING SPECIFICATIONS AND STANDARDS
Development of Piping Specifications and Standards: Creating detailed specifications and standards for the selection, fabrication, and installation of steam piping systems. These standards ensure consistency, quality, and compliance with industry regulations, helping to streamline the entire project from design through to commissioning

PIPE SIZING AND HYDRAULIC CALCULATIONS
Pipe Sizing and Hydraulic Calculations: Calculating the appropriate steam pipe sizes and conducting hydraulic analysis to achieve desired flow rates while minimizing pressure drops. This step ensures that the system operates efficiently and within the design parameters while reducing energy costs and potential system failures.

3D MODELING AND DESIGN
3D Modeling and Design: Utilizing software such as PDS, PDMS, or AutoPlant to create detailed 3D models of steam piping systems. These models provide a better visualization of the system layout and help improve accuracy, coordination, and efficiency in the design process, minimizing errors and conflicts during construction.

ISOMETRIC/FABRICATION/ERECTION DRAWINGS
Isometric/Fabrication/Erection Drawings: Preparing detailed isometric, fabrication, and erection drawings that guide the manufacturing and installation of steam piping systems. These drawings ensure that the system is built according to design specifications and that all components are properly aligned for efficient installation.
Steam Piping Design Services
Piping Design and Drafting: Creating detailed CAD drawings and design calculations for steam piping systems used in power plants, refineries, and other industrial facilities.
Pipe Stress Analysis: Performing static and dynamic stress analysis using software like CAESAR II to ensure the steam piping system can withstand operational and environmental stresses.
3D Modeling and Design: Using software such as PDS, PDMS, or Auto Plant to create 3D models of steam piping systems for better visualization and accuracy.
Isometric/Fabrication/Erection Drawings: Preparing detailed drawings for the fabrication and installation of steam piping systems.
Support Detail Drawing Preparation: Designing and detailing the necessary supports for the steam piping system to ensure stability and safety.
Project Management: Managing the entire steam piping design project from initial conceptualization through fabrication and commissioning.
Compliance with Standards: Ensuring that the design complies with relevant standards such as ASME B31.1 for power piping and ASME B31.3 for process piping.
BILL OF MATERIAL, INSULATION & EXPANSION JOINTS
Challenges in Steam Piping Design
Designing steam piping systems comes with a variety of challenges that require careful planning, expertise, and experience to overcome. Steam piping is a critical component in many industrial processes, and even small issues can lead to significant operational disruptions or safety risks. Here are some common challenges in steam piping design:
1. Pressure and Temperature Management
Steam piping systems need to handle high-pressure and high-temperature steam. Managing these variables effectively is crucial to ensure that the system operates safely and efficiently. Incorrect pressure or temperature settings can lead to pipe fatigue, leaks, or failures.
Challenge: Maintaining the correct balance of pressure and temperature while ensuring the system remains durable under varying conditions.
Solution: Careful design and selection of materials that can withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved, along with detailed calculations to ensure the system’s longevity and safety.
2. Pipe Sizing
Choosing the right pipe size is essential to maintaining steam flow efficiency and avoiding energy losses. Oversized or undersized pipes can lead to problems like excessive pressure drops or inadequate steam supply.
Challenge: Properly sizing pipes to accommodate the flow rate and steam pressure while minimizing energy losses and ensuring system efficiency.
Solution: Use advanced calculation methods and modeling software to accurately determine the optimal pipe diameter, ensuring effective steam distribution.
3. Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Steam piping is subject to thermal expansion and contraction due to the heat changes in the steam. This can place strain on the pipes and their connections, leading to misalignment, stress, or even damage to the system.
Challenge: Designing the system to accommodate these thermal movements and prevent damage to the piping infrastructure.
Solution: Incorporating expansion loops, bends, or flexible joints in the design to absorb thermal movement while ensuring the system remains structurally sound.
4. Condensation Management
As steam cools down and condenses, it can cause water hammer and damage the piping system. Effective drainage and venting systems need to be included to manage condensation and prevent blockages.
Challenge: Designing an efficient system to handle condensate drainage without causing operational disruptions or damage.
Solution: Implementing proper condensate return systems, traps, and venting mechanisms to manage condensation and prevent the buildup of water in the piping.
5. Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for steam piping is vital to ensure durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Different materials have different strengths and weaknesses when exposed to high temperatures, pressures, and steam conditions.
Challenge: Selecting materials that can withstand the corrosive effects of steam and ensure a long-lasting system.
Solution: Evaluating the conditions of each application and selecting corrosion-resistant and high-temperature materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloys designed for steam service.
6. System Complexity and Layout
Steam piping systems can often be complex, requiring intricate layouts that optimize space while accommodating other elements like valves, pumps, and other equipment. In some cases, the installation space may be limited, complicating the design further.
Challenge: Designing a piping layout that is both space-efficient and easily accessible for maintenance, all while ensuring operational efficiency.
Solution: Developing detailed 3D models of the piping layout to identify the best route, prevent interference with other systems, and ensure that the design is easy to implement and maintain.
7. Compliance with Codes and Regulations
Steam piping systems must comply with various codes, standards, and safety regulations. Non-compliance can lead to issues, penalties, or operational shutdowns.
Challenge: Navigating the complex array of codes and regulations governing steam piping design.
Solution: Staying updated with local and international standards (such as ASME, ASTM, and ANSI) and ensuring the design meets all required safety, environmental, and performance criteria.
8. Energy Efficiency
Steam systems are typically energy-intensive, and optimizing their energy efficiency is a critical challenge. An inefficient steam piping system can lead to unnecessary energy consumption, increased operational costs, and environmental impact.
Challenge: Designing a system that minimizes energy losses, ensures proper steam distribution, and reduces operational costs.
Solution: Focusing on system efficiency through insulation, minimizing leaks, and designing for optimal steam pressure and flow control.
9. Maintenance and Accessibility
Steam piping systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent failures. A key challenge is designing the system to allow for easy maintenance and accessibility without disrupting daily operations.
Challenge: Ensuring that the piping system is easy to maintain and repair while minimizing downtime and operational disruption.
Solution: Incorporating access points, valves, and inspection ports that allow easy monitoring, maintenance, and repair work.



